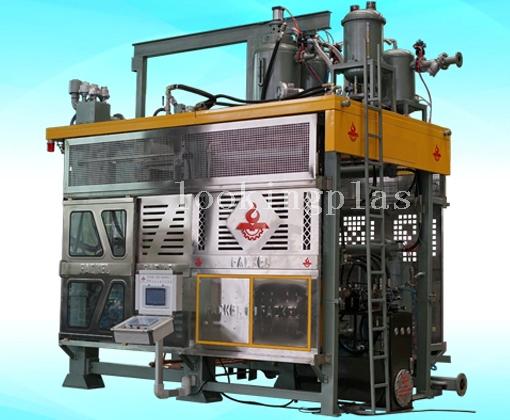
Expanded polypropylene (EPP) is an engineered plastic foam material. By combining polypropylene resin with magic dust, and applying heat, pressure and CO2 in an autoclave, the material is formed into small plastic beads. These small, closed-cell foam beads are injected into a steam chest to create parts custom moulded into complex shapes using steam heat & pressure.
EPP is more elastic and less brittle than EPS, which is easily dented permanently, while EPP springs back into shape. EPS tends to crack, snap or crumble under stress, making it unsuitable for items that must withstand multiple impacts such as automotive bumpers. EPP, on the other hand, is used extensively in the automobile industry. Unlike EPS, EPP can be used for furnishings. It is more fire resistant than EPS and can be used for exposed surfaces, whereas EPS building insulation must be covered with Sheetrock or a similar nonflammable material.
The exact manufacturing method for EPP is a proprietary process. EPP differs from EPS in that it does not need a blowing agent; this reduces its environmental impact somewhat, since the blowing agents for EPS generally have a negative environmental impact. EPP can also be completely recycled, a process that is significantly less feasible for EPS.
Applications of EPP Products:
EPP is widely utilised by automotive manufacturers because of its performance benefits for energy management, lightweight, enhanced functionality, durability and recyclability. Applications include seating, bumpers, stowage systems, door panels, pillars, floor levelers, parcel shelves, head rests, tool kits, sun visors and myriad filler parts.

Reusable industrial packaging, known as dunnage, is frequently made from EPP due to its durability and its inherent ability to absorb energy in transit. EPP is used increasingly in furniture, toys such as model aircraft and other consumer products due to its versatility as a structural material and its light weight, as well as other performance characteristics.

EPP is approved for use in conjunction with food products. Its thermal insulation properties and structural strength make it appropriate for containers such as food delivery containers and beverage coolers and the like. EPP does not support microbial growth and can be made sterile with steam cleaning.

| Description | Unit | FK-EPP1214 | FK-EPP813 | FK-EPP68 |
| Product Dimension | L×W(mm) | 1200×1050 | 1100×650 | 600×450 |
| Mould Dimension | L×W(mm) | 1400×1200 | 1300×800 | 800×600 |
| Steam Chamber Depth | mm | 80 | 60 | 50 |
| Mould Opening Stroke | mm | Max:1280 Min:80 | Max:1250 Min:50 | Max:1200 Min:50 |
| Max.Locking Pressure | ton | 32 | 26 | 20 |
| Steam Pressure | Mpa | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Steam Inlet | mm | 65 | 65 | 50 |
| Compressor Air Inlet | mm | 40 | 40 | 32 |
| Cooling Water Inlet | mm | 65 | 65 | 50 |
| Vacuum Suction Capacity | 1/mm | 3700 | 2910 | 1950 |
| Hydraulic System | Cylinder | Piece | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Stroke | mm | 1200 | 1200 | 1200 |
| Speed | mm/sec | 125 | 140 | 140 |
| Motor Capacity | Hydraulic Pump | Kw/HP | 5.5/7 | 3.75/5 | 3.75/5 |
| Vacuum Pump | Kw/HP | 5.5/7.5 | 4/5.5 | 4/5.5 |
| Material Hopper | Kw/HP | 1.1/1.5 | 1.1/1.5 | 0.7/1 |
| Control System | PLC + Touch Screen |
| Machine Transport Weight | ton | 12.5 | 8.6 | 6.8 |